
How to Use Bitcoin QR Codes: Step-by-Step Guide
Bitcoin QR codes have revolutionized the way cryptocurrency transactions occur, eliminating the need to manually type long wallet addresses and reducing the risk of costly errors. Whether you’re a seasoned crypto investor or just beginning your journey into digital assets, understanding how to use Bitcoin QR codes is essential for secure and efficient transactions. These simple square barcodes contain encoded wallet information that can be scanned instantly using any smartphone, making peer-to-peer payments and receiving funds faster than ever before.
In today’s cryptocurrency ecosystem, QR codes serve as a bridge between complex blockchain technology and user-friendly interfaces. They’ve become the standard method for sharing wallet addresses across exchanges, wallets, and payment processors. This comprehensive guide will walk you through every aspect of Bitcoin QR codes, from understanding their basic functionality to implementing them safely in your daily crypto transactions. Whether you’re receiving payments, sending funds, or managing multiple wallets, mastering QR code usage will significantly enhance your cryptocurrency experience.
What Are Bitcoin QR Codes and How Do They Work
A Bitcoin QR code is a two-dimensional barcode that encodes your wallet address and optionally includes transaction details like the amount requested and payment description. QR stands for Quick Response, referring to the code’s ability to be read quickly by cameras and scanning applications. When you generate a bitcoin QR code, it transforms your alphanumeric wallet address—typically a long string of 26-35 characters—into a visual format that’s much easier to share and scan.
The technical mechanism behind Bitcoin QR codes relies on standardized encoding protocols. Your wallet address is encoded using the QR code standard (usually ISO/IEC 18004), which stores data across multiple layers of the square pattern. Bitcoin-specific QR codes often follow the BIP21 standard, which allows for additional parameters such as the amount, label, and message. When someone scans your QR code using their smartphone camera or a dedicated QR scanner app, the device instantly decodes the information and presents it in a readable format, ready for transaction processing.
Modern Bitcoin wallets automatically generate QR codes for each address, displaying them prominently in the receive section of the application. The beauty of this system lies in its simplicity and universality—any smartphone with a camera can scan a QR code, and any Bitcoin wallet application can process the encoded information. This standardization has made Bitcoin transactions more accessible to mainstream users while maintaining the security and precision that cryptocurrency demands.
Why Use QR Codes for Bitcoin Transactions
Using bitcoin QR codes offers numerous advantages over traditional methods of sharing wallet addresses. The primary benefit is accuracy—manually typing a 34-character wallet address leaves substantial room for human error, and a single mistyped character could send your funds to an entirely different address, resulting in irreversible loss. QR codes eliminate this risk by ensuring that the exact address is captured without any possibility of transcription errors.
Convenience represents another compelling reason to adopt QR code technology. Rather than copying and pasting long addresses or writing them down, you can simply point your smartphone camera at a QR code and complete the process in seconds. This friction-free experience is particularly valuable in retail environments, at cryptocurrency meetups, or when conducting business transactions where speed matters. For merchants accepting Bitcoin payments, displaying a QR code at checkout is significantly more practical than asking customers to manually enter wallet information.
Security benefits also make QR codes attractive for cryptocurrency users. When you share a QR code instead of typing your address verbally or writing it on paper, you reduce exposure to shoulder surfing and other observation-based attacks. Additionally, QR codes can be encrypted or protected with additional security layers in advanced implementations. For those monitoring their bitcoin forecast 2025 and managing multiple investment positions, the ability to quickly and accurately share addresses across different platforms and wallets becomes invaluable.
Mobile optimization is another factor driving QR code adoption. As cryptocurrency becomes increasingly mobile-first, with users managing portfolios through smartphones and tablets, QR codes provide the perfect interface between physical and digital worlds. You can share a QR code printed on paper, displayed on a screen, or embedded in digital communications, and it will work seamlessly across all platforms and devices.
Step-by-Step Guide to Receiving Bitcoin via QR Code
Step 1: Open Your Bitcoin Wallet Application
Begin by launching your cryptocurrency wallet on your smartphone or computer. Popular options include Electrum, Coinbase, Kraken, and hardware wallet companions like Ledger Live. If you’re new to Bitcoin, you may want to start with a user-friendly mobile wallet before progressing to more advanced options. Ensure your wallet application is up to date with the latest security patches and features.
Step 2: Navigate to the Receive Section
Look for a “Receive” or “Request” button within your wallet interface. This section displays your wallet’s public address and generates the corresponding QR code. Different wallet applications organize this differently, but most place the receive function prominently in the main menu or navigation bar. Some wallets allow you to create multiple receive addresses, which is recommended for privacy reasons.
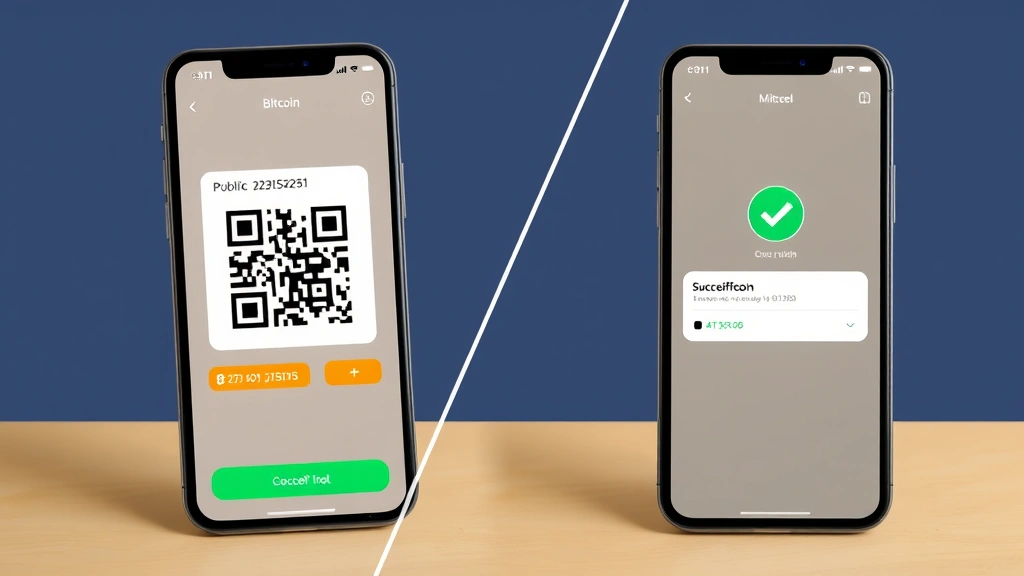
Step 3: Display Your QR Code
Once you’ve accessed the receive section, your wallet will display your public Bitcoin address alongside its QR code representation. The QR code appears as a square pattern containing black and white modules. Many wallets allow you to customize this display—you can zoom in for easier scanning, copy the address to your clipboard, or share it directly through messaging applications. Some advanced wallets enable you to set a specific amount in the QR code, automatically populating the payment request.
Step 4: Share Your QR Code
You can share your QR code in multiple ways: take a screenshot and send it via email or messaging apps, print it for physical transactions, display it on your computer screen, or share a link to your public address. Remember that your public address is meant to be shared—it’s impossible to spend funds using only the public address. The private key, which you must never share, is what actually controls your Bitcoin.
Step 5: Monitor the Transaction
Once someone scans your QR code and sends Bitcoin, you’ll receive a notification in your wallet application. The transaction will appear in your transaction history with pending status initially, then confirmed status once it’s been added to the blockchain. Most wallets allow you to track confirmations in real-time, providing transparency about when your funds are fully settled.
How to Send Bitcoin Using QR Codes
Sending Bitcoin using a QR code is equally straightforward and perhaps even more practical than receiving. This method is particularly useful when paying merchants or transferring funds to friends who have their wallet address displayed as a QR code.
Step 1: Access the Send Function
Open your Bitcoin wallet and locate the “Send” or “Pay” button. This initiates the payment process and prepares your wallet to construct a transaction. Ensure you have sufficient Bitcoin in your wallet to cover both the amount you’re sending and any applicable network fees.
Step 2: Activate the QR Code Scanner
Most Bitcoin wallets include a built-in QR code scanner accessible from the send screen. Look for a camera icon or “Scan QR Code” button. When you tap this, your device will request camera permission and activate the camera interface. Grant the necessary permissions to allow your wallet to access your device’s camera.
Step 3: Point Your Camera at the QR Code
Aim your smartphone’s camera at the recipient’s QR code. Hold your device steady at a distance of 4-6 inches from the QR code for optimal scanning. The camera will automatically detect the code and decode it within seconds. Ensure adequate lighting for faster recognition, though most modern scanners can read codes in various lighting conditions.
Step 4: Verify the Address
Once scanned, your wallet will display the recipient’s address in a readable format. Always verify that the decoded address matches what you expect before proceeding. This verification step is crucial for security—verify the first and last few characters of the address to ensure no malicious substitution has occurred. Some addresses may include additional information like an amount or payment description.
Step 5: Enter the Transaction Amount
If the QR code didn’t include a specific amount, you’ll need to manually enter how much Bitcoin you wish to send. Most wallets display the amount in both Bitcoin and your local currency for clarity. Review this carefully before confirming. Consider current is bitcoin going to crash predictions and market conditions if timing is important for your transaction.
Step 6: Set Network Fees
Choose your preferred network fee, which determines how quickly your transaction will be confirmed. Higher fees result in faster confirmation, while lower fees may take longer. Many wallets offer preset options like “slow,” “standard,” or “fast.” Review the estimated confirmation time and fee amount before proceeding.
Step 7: Confirm and Send
Review all transaction details one final time, then confirm and send. Your wallet will sign the transaction using your private key and broadcast it to the Bitcoin network. You’ll receive a confirmation showing your transaction ID (TXID), which you can use to track the transaction on a blockchain explorer.
Security Considerations for Bitcoin QR Codes
While Bitcoin QR codes are generally secure, several important considerations can enhance your safety when using them. The most critical principle is understanding what information QR codes contain: your public address is safe to share, but your private key QR code must be protected with extreme care.
Protecting Your Private Key QR Code
Many wallets allow you to export your private key as a QR code for backup purposes. This QR code is equivalent to your wallet’s master key and grants complete access to your funds. Never photograph this QR code or display it on an unencrypted screen. Store any physical backups in a secure location like a safe deposit box, and consider splitting backup information across multiple secure locations. If someone obtains your private key QR code, they can access and drain your entire wallet instantly.
Verifying QR Codes Before Scanning
When receiving a QR code from someone else, especially in online contexts, exercise caution. Malicious actors can create fraudulent QR codes that direct you to scam websites or direct payments to their addresses. Always verify the source of any QR code and cross-check the decoded address with information from trusted sources. If receiving payment instructions from a business or contact, confirm directly with them through established communication channels.
Using Reputable Wallet Applications
Download your Bitcoin wallet only from official sources—the App Store for iOS or Google Play for Android. Verify that you’re installing the legitimate application by checking the developer name and reading recent user reviews. Malicious apps can display fake QR codes or steal scanning data. Popular wallets like Electrum, Coinbase, and Kraken have established track records and security audits.
Network Security While Scanning
When scanning QR codes, ensure you’re using secure networks, particularly when conducting transactions. Avoid scanning and processing payments on public WiFi networks without a VPN, as attackers could potentially intercept your connection. For large transactions, consider using your home network or mobile data for enhanced security. Some advanced wallets support hardware wallet integration, which adds additional security layers by requiring physical confirmation of transactions.
Keeping Your Device Secure
Your smartphone or computer is your gateway to Bitcoin transactions, so maintaining its security is paramount. Install security updates promptly, use strong passwords or biometric authentication, enable two-factor authentication where available, and consider installing reputable antivirus software. Regularly review your wallet’s transaction history for unauthorized activity.
Troubleshooting Common QR Code Issues
Despite their reliability, users sometimes encounter issues with Bitcoin QR codes. Understanding common problems and their solutions can help you resolve difficulties quickly.
QR Code Won’t Scan
If your device cannot scan a QR code, several factors might be responsible. First, ensure adequate lighting—dim environments make scanning difficult. Clean your device’s camera lens to remove dust or smudges. Try moving closer or farther from the QR code to find the optimal focus distance. If the QR code is printed, ensure it hasn’t been damaged or faded. Some older devices may have camera limitations; try using a dedicated QR code scanning app instead of your wallet’s built-in scanner. Verify that your wallet application has camera permissions enabled in your device settings.
Address Mismatch After Scanning
If the decoded address appears different from what you expected, stop immediately and do not proceed with the transaction. This could indicate a malicious QR code or a technical error. Delete the transaction, verify the QR code source, and try scanning again. If the problem persists, contact the address owner directly through alternative communication channels to confirm the correct address.
Transaction Not Appearing in Wallet
After scanning a QR code and sending funds, transactions should appear in your wallet within minutes. If hours pass without any transaction record, verify that you actually confirmed the transaction—sometimes the process is interrupted unintentionally. Check your network connection and ensure your wallet is synchronized with the blockchain. Restart your wallet application and check again. If the transaction still doesn’t appear, contact your wallet provider’s support team with your transaction ID.
Compatibility Issues Across Wallets
Most Bitcoin QR codes follow standard formats and work across different wallet applications. However, some wallets or older versions may not support certain QR code features. If you’re having compatibility issues, ensure your wallet application is updated to the latest version. If problems persist, try using a different wallet application to verify whether the issue is specific to one wallet or a broader problem with the QR code itself.
QR Code Not Displaying Correctly
If your wallet generates a QR code that appears distorted, pixelated, or incomplete, try refreshing the screen or restarting your wallet application. Some devices with lower display resolution may struggle with QR code rendering. Zoom in on the QR code to see if it’s actually readable despite appearing small on your screen. If the problem continues, try generating a new QR code or exporting your address in text format instead.
Advanced QR Code Features and Options
Beyond basic sending and receiving, several advanced features can enhance your use of Bitcoin QR codes. These options are particularly valuable for businesses, frequent traders, and users managing complex cryptocurrency portfolios related to investments like BlackRock Bitcoin ETF 2025 predictions.
BIP21 URI Standard
The BIP21 standard allows QR codes to encode more than just a wallet address. These enhanced QR codes can include the payment amount, recipient name, and transaction description. When you scan a BIP21-compliant QR code, your wallet automatically populates these fields, reducing manual entry and potential errors. Many modern wallets support this standard, making it ideal for invoices and payment requests. For example, a merchant could generate a QR code that encodes both their address and the exact amount owed, streamlining the checkout process.
Dynamic QR Codes
Dynamic QR codes can be updated after creation, unlike static QR codes which are permanent once generated. Some advanced services allow you to create dynamic QR codes that redirect to different addresses based on scanning device, time, or other parameters. While not yet common in basic Bitcoin wallets, dynamic QR codes offer potential for more sophisticated payment systems and marketing applications. However, this technology introduces additional complexity and potential security considerations.
Multi-Signature Wallet QR Codes
For enhanced security, multi-signature wallets require approval from multiple parties before funds can be moved. These wallets can generate QR codes that include multi-signature information, allowing other wallet holders to scan and verify transaction details. This feature is particularly valuable for business accounts, family wealth management, or cryptocurrency investment groups where shared responsibility and oversight are important.
Batch QR Code Generation
Some wallets and services allow you to generate multiple QR codes in bulk. This is useful for merchants who want to create QR codes for different transactions or invoices, or for businesses accepting Bitcoin at multiple locations. Batch generation saves time and ensures consistency across all your payment collection methods.
QR Code Customization
Advanced wallet applications and third-party services allow you to customize QR code appearance—adding logos, changing colors, or adjusting error correction levels. While customization can enhance brand recognition for businesses, it’s important not to compromise QR code functionality. Always test customized QR codes thoroughly before using them for actual transactions. Remember that Trump Bitcoin news and regulatory developments may affect how businesses can market their cryptocurrency payment options.
Cold Storage Address QR Codes
For long-term Bitcoin storage, many users employ cold storage solutions like hardware wallets. These devices can generate QR codes for their public addresses, allowing you to receive Bitcoin without ever exposing your private keys to internet-connected devices. This approach combines the convenience of QR codes with the security of offline storage, making it ideal for serious investors managing substantial cryptocurrency holdings.
Integration with Payment Processors
Payment processors and point-of-sale systems for Bitcoin often feature QR code integration. These systems can generate merchant QR codes that route payments through their platform, providing additional services like currency conversion, instant settlement, or integration with accounting software. This integration enables seamless Bitcoin acceptance for retail businesses while maintaining the simplicity of QR code scanning.

FAQ
Can someone steal my Bitcoin by scanning my QR code?
No, scanning your public address QR code cannot steal your Bitcoin. Your public address is meant to be shared—it only allows others to send you funds. The private key QR code, however, is equivalent to your wallet’s master password and must be kept secure. Never share your private key QR code with anyone.
What’s the difference between a public address and a private key QR code?
A public address QR code can be freely shared and only allows others to send you Bitcoin. A private key QR code grants complete access to your funds and should be guarded as carefully as your password or PIN. Your wallet should clearly distinguish between these two types of QR codes.
Can I use the same QR code multiple times?
Yes, you can use the same public address QR code unlimited times to receive Bitcoin from different sources. However, for privacy reasons, many wallet applications recommend using a different address for each transaction. Most wallets automatically generate new addresses for this purpose.
Are Bitcoin QR codes the same across all wallet applications?
Bitcoin QR codes follow standardized protocols, so a QR code generated by one wallet application can typically be scanned by any other Bitcoin wallet. However, some advanced features or wallet-specific information might not be universally compatible. Stick with widely-used wallets to ensure maximum compatibility.
What if I accidentally scan a malicious QR code?
Simply scanning a QR code cannot harm your device or compromise your wallet. However, if the decoded information directs you to a fraudulent website or contains a malicious address, you could lose funds if you proceed with a transaction. Always verify decoded information before confirming any payment.
Can I generate a QR code for receiving Bitcoin without a wallet?
Technically, you need a valid Bitcoin address to generate a QR code, which requires having a wallet. However, you don’t necessarily need to install a full wallet application—online wallet generators and services can create QR codes for addresses. Be cautious with online tools and only use reputable, well-established services.
How do I know if my QR code is secure?
A public address QR code is inherently secure because it contains no sensitive information. To verify security, you can decode the QR code using any online QR decoder and confirm that it matches your expected Bitcoin address. For maximum security with private key QR codes, store them offline in secure locations like safes or safety deposit boxes.
What happens if someone modifies a printed QR code?
If a QR code is physically altered, it may become unreadable, or it could potentially be modified to direct to a different address. This is why it’s important to obtain QR codes from trusted sources. If you’re printing QR codes for use, keep them in secure locations and verify them periodically.
